2-Legged OAuth
I did not change the process flow of original 3-legged OAuth to support 2-legged OAuth. I made a small change to user authorization step described at http://oauth.net/core/1.0/#auth_step2. Two additional parameters are added to support 2-legged OAuth: user_id and cgl_oauth_signagure. See http://zhenhua-guo.blogspot.com/2009/04/oauth-myproxy-integration-prototype.html for more information.
Integrity check:
- check trust relationship between service provider and client app.
Currently, just check whether the clien app has been registered at service provider with correct information. - check pre-assigned priviledges to client app by user (this only applies to 2-legged OAuth)
A client app must have been granted access priviledge before it can access user data stored at service provider
Implementation
Client
Client App
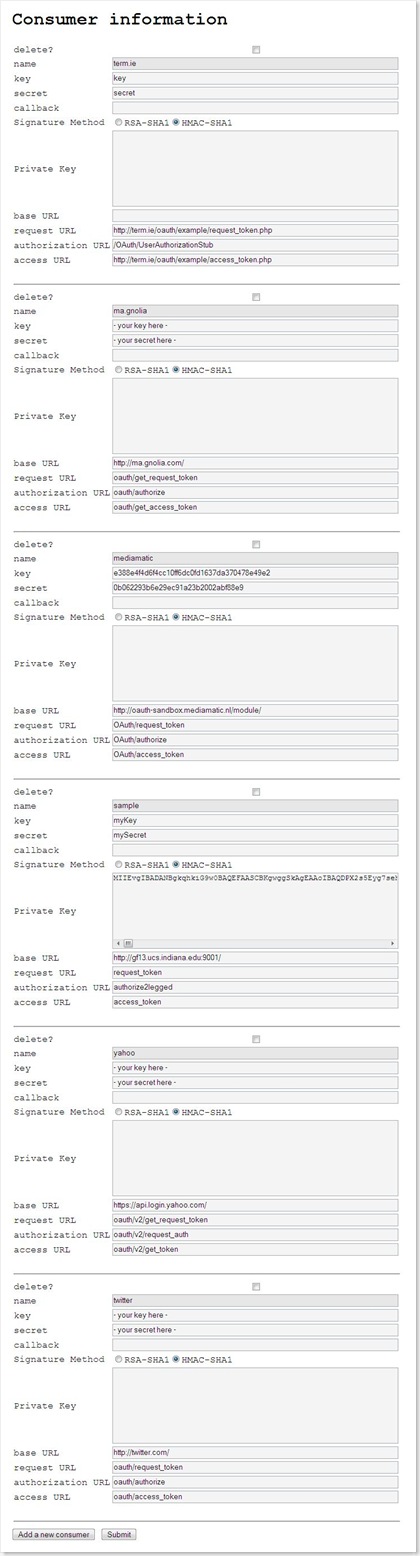
Most important information about a client application includes:
- name
- description
- consumer key
See http://oauth.net/core/1.0/#anchor6 - consumer secret
See http://oauth.net/core/1.0/#anchor6 - callback URL
The address to which user is redirected after data owner accepts access request. - signature method
HMAC-SHA1 or RSA-SHA1. Currently, only use RSA-SHA1. - private key
Used to generate signature - request token URL
See http://oauth.net/core/1.0/#auth_step1 - authorization URL
See http://oauth.net/core/1.0/#auth_step2 - access token url
See http://oauth.net/core/1.0/#auth_step3
A list of client applications is listed and users can add or remove client applications.
Snapshot:
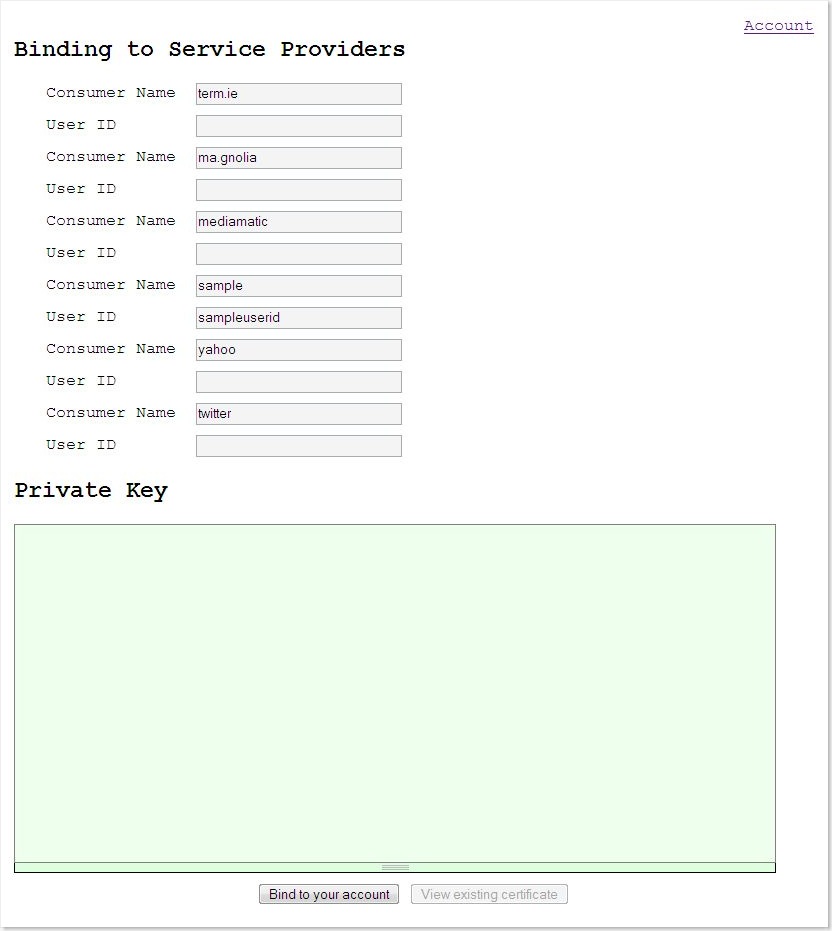
Users can set userid that is used during invocation of remote service. Also to make it possible for client app to access user data at service provider, the user should upload private key to client app so that correct signature can be generated during OAuth process.
Tables
Four tables in database:
- oauth_consumer_users
- This table stores basic user account information. Currently,
username and password are the only two attributes. - oauth_consumer_settting
- This table stores private key belonging to each user. The private key is used during OAuth authorization process.
- oauth_consumer_spbinding
- This table stores binding relationships between users and service providers. So the information in this table is used when client app invokes remote service on behalf of user. Currently the main information is the user id that is used by service provider. In other words, a mapping from local user id to remote user id is established.
- oauth_consumers
- This table stores information of client applications.
Service Provider
Service provider provides interfaces that can be used by third party applications to access users' data.
For application developer
Client application registration
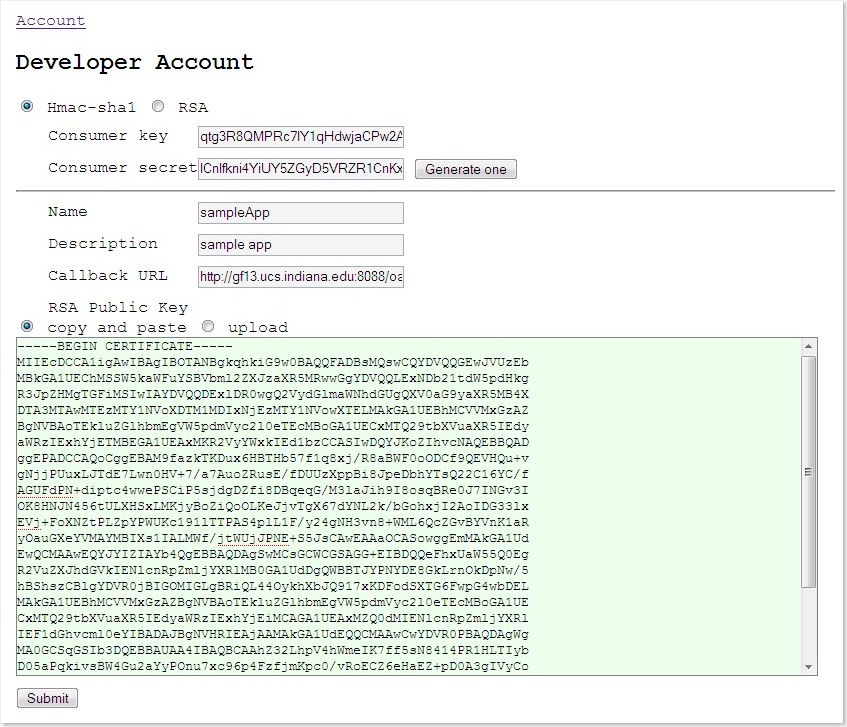
To register a client app, developers need to follow these instructions:
- apply for a consumer key/secret pair.
- type informatoin about the clien app including
- app name
- app description
- app callback URL
- public key
In my implementation, the registration page can be accessed at <baseurl>/oauthServer-0.1/developerAcc.jsp after our system is installed.
Screenshot:
For common users
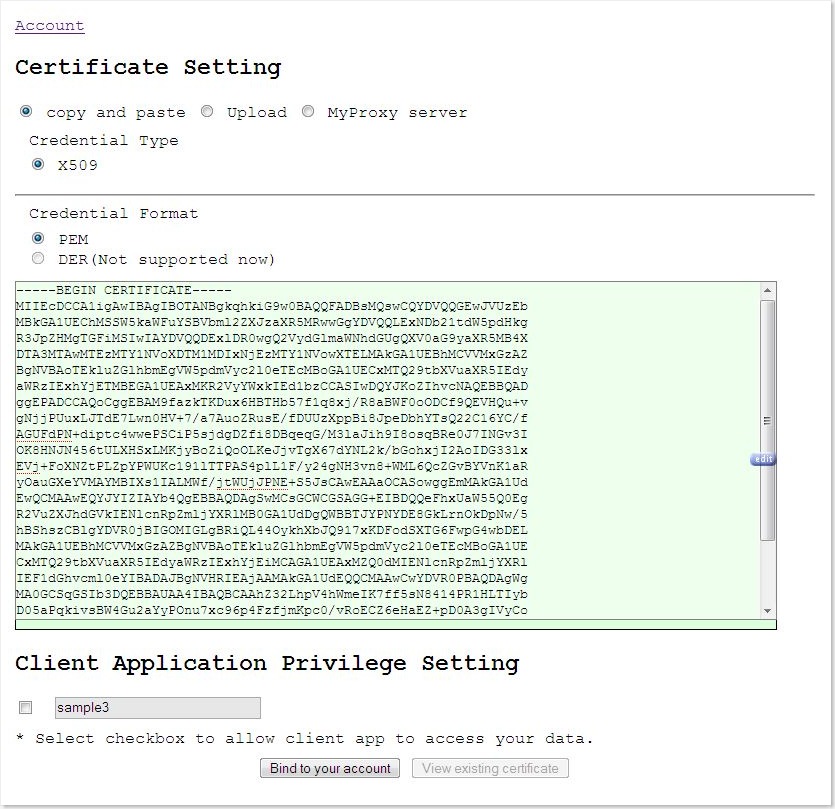
Some third-party applications may want to access users' data stored at service provider. In 3-legged OAuth, the service provider redirects the user to a web page where the access request can be accepted or denied. In 2-legged, no user intervenetion is involved, so the authorization setting must be preset.
In our system, we provide a way for common users to grant priviledge to and revoke priviledge from client (3rd party) applications. Also the user must upload a public key against which signature of requests receieved from client app can be verified.
Snapshot
Tables
- oauth_server_users
- Basic user account information. Currently, just includes user name and password.
- oauth_server_setting
- stores public key extracted from myproxy server or direct upload.
- oauth_server_dev
- Stores information of registered client applications.
- oauth_server_userappauth
- Stores information of priviledge authorization set by each user.







